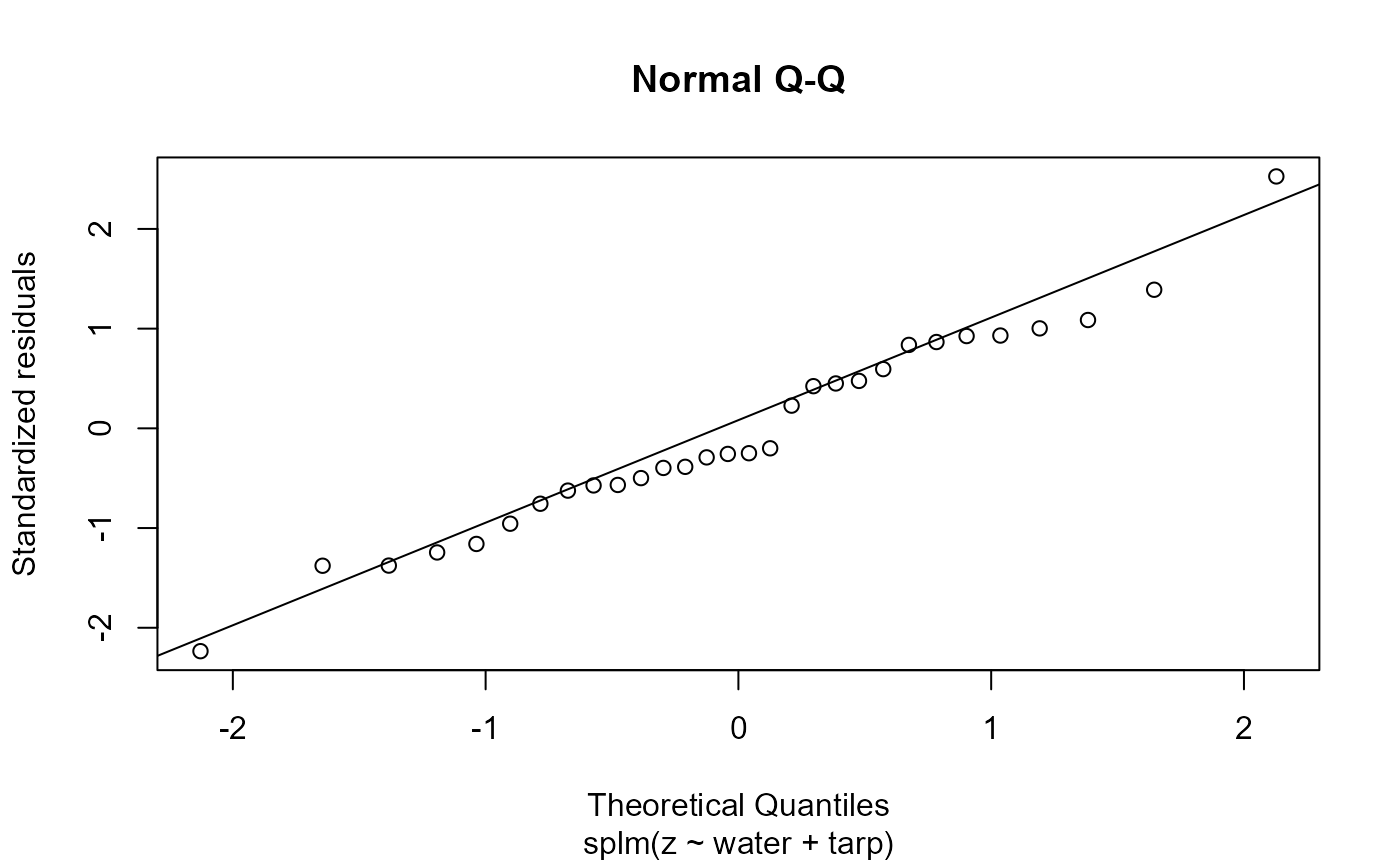
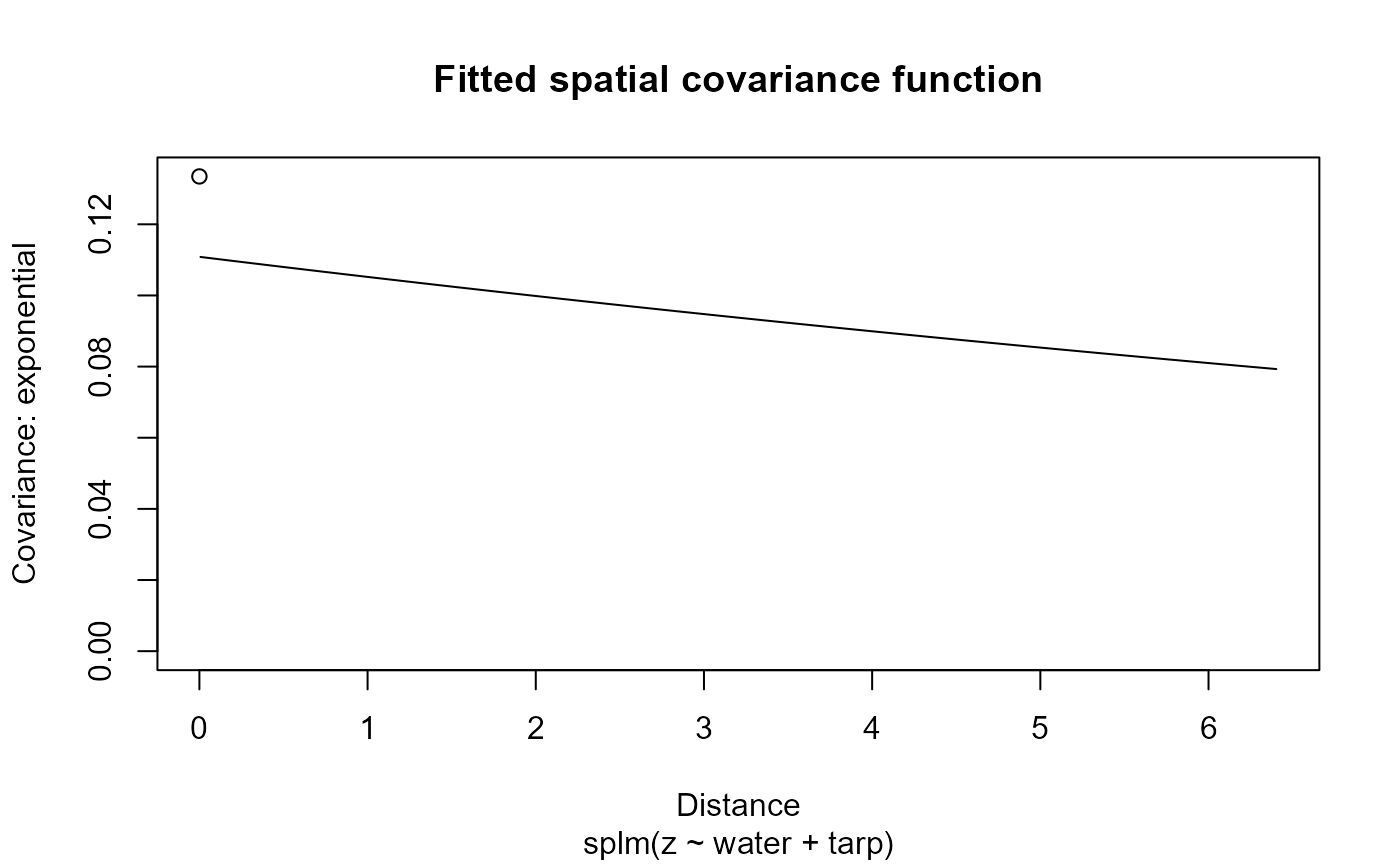
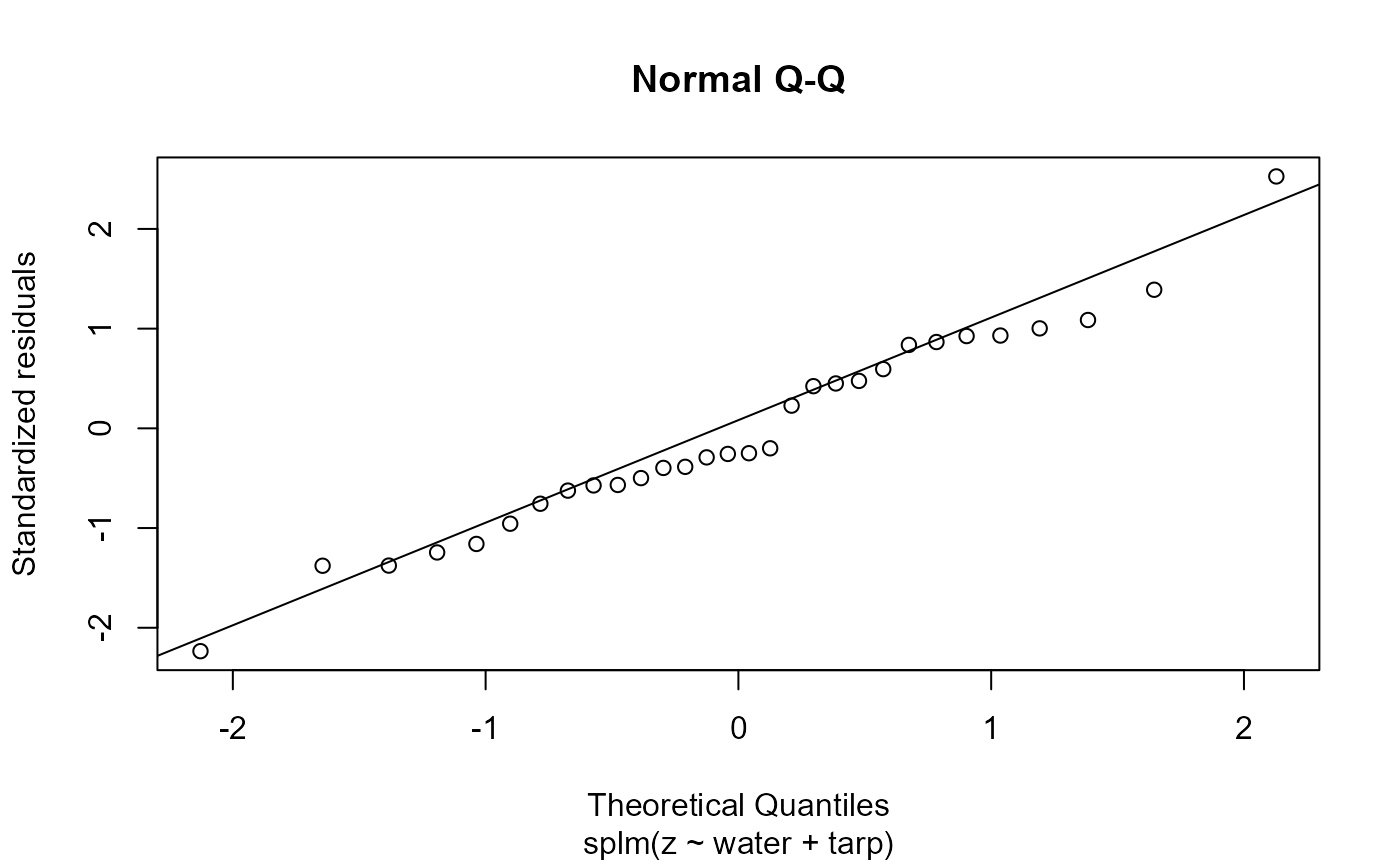
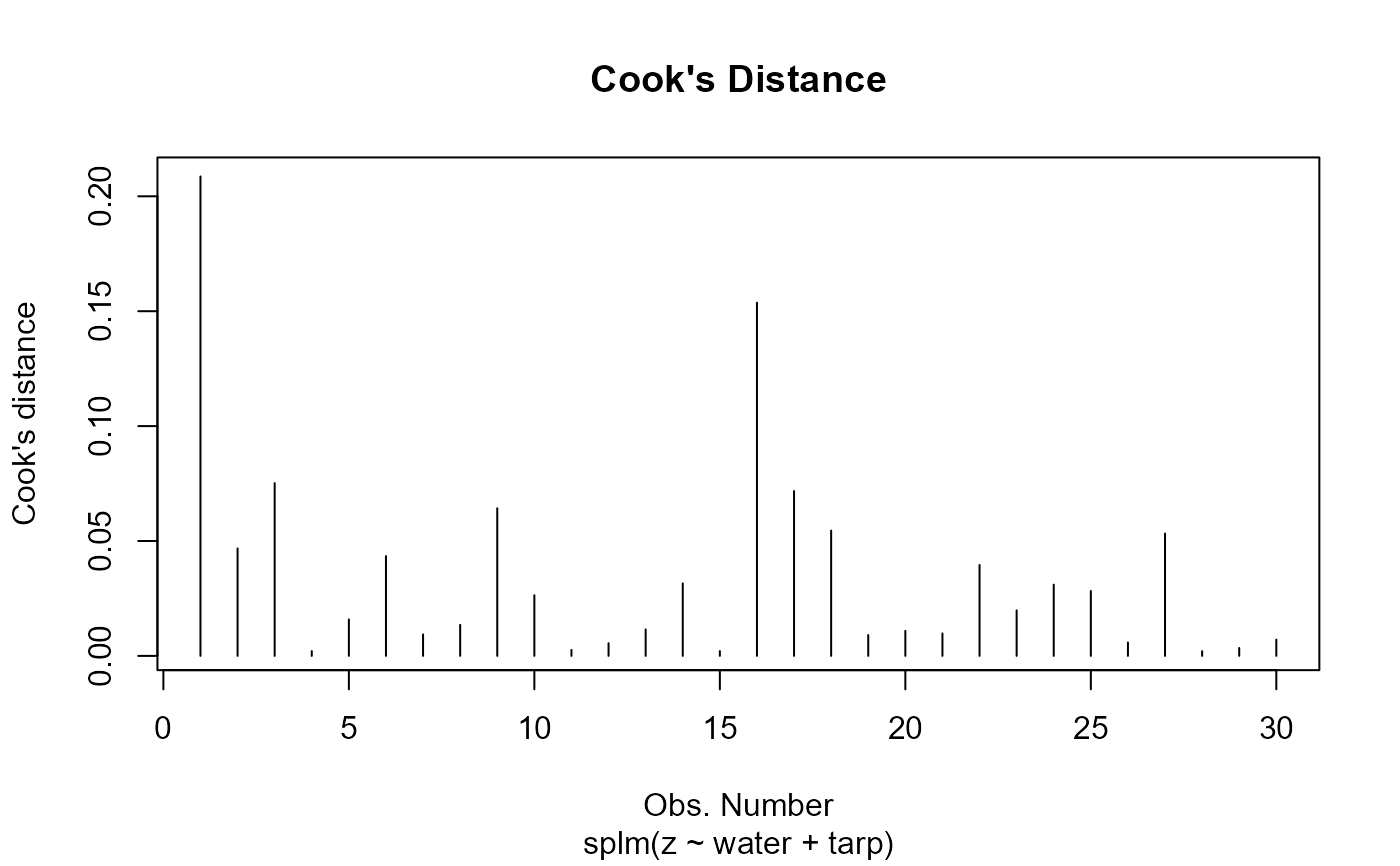
Plot fitted model diagnostics such as residuals vs fitted values, quantile-quantile, scale-location, Cook's distance, residuals vs leverage, Cook's distance vs leverage, a fitted spatial covariance function, and a fitted anisotropic level curve of equal correlation.
Arguments
- x
A fitted model object from
splm(),spautor(),spglm(), orspgautor().- which
An integer vector taking on values between 1 and 7, which indicates the plots to return. Available plots are described in Details. If
whichhas length greater than one, additional plots are stepped through in order using<Return>. The default forsplm()andspglm()fitted model objects iswhich = c(1, 2, 7). The default forspautor()andspgautor()fitted model objects iswhich = c(1, 2).- ...
Other arguments passed to other methods.
Value
No return value. Function called for plotting side effects.
Details
For all fitted model objects,, the values of which make the
corresponding plot:
1: Standardized residuals vs fitted values (of the response)
2: Normal quantile-quantile plot of standardized residuals
3: Scale-location plot of standardized residuals
4: Cook's distance
5: Standardized residuals vs leverage
6: Cook's distance vs leverage
For splm() and spglm() fitted model objects, there are two additional values of which:
7: Fitted spatial covariance function vs distance
8: Fitted anisotropic (or isotropic) level curve of equal correlation